Belt, Chain, and Gear Drives: Which Is Better For You?
The need to produce more energy keeps edging up with the growing demand for industrial and commercial space. In any industry, motors and turbines generate rotational motion to run various tasks.
The main power transmission systems in the market include belt drives, chain drives, and gear systems. This post outlines the main pros and cons of each.
The Belt Technology
Belt drives are some of the common devices for transmitting motion from one shaft to another using pulley system. The system comprises of a looped strip from a flexible material that help link rotating shafts.
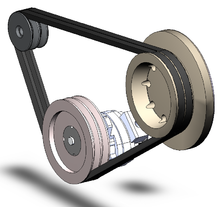
Today, there are many kinds of drives including the V-belt, cogged belt, and synchronous belt. The most important things when selecting a belt include the power to be transmitted, shaft's velocity, the direction of belt motion, and service condition.
|
Pros |
Cons |
|
|
Chain transmission
Like the name suggests, the chain drives operate through a system of chain links that connect via a set of toothed sprockets. Unlike with the belt system, the chain system does not suffer slipping.

The main issue with the chains is that they are considered ideal for small center distances of about three meters. However, there are some systems engineered to support chain systems of up to 8 meters. The chain system is mainly used for the following three tasks:
- Power transmission
- Conveying materials
- Timing
|
Pros |
Cons |
|
|
Gear power transmission

Gear drives hold a special place in the world of power transmission. They are the most preferred model of power transmission over short distances. Unlike the belts or chains, the system of gears is relatively simple; teeth on a plant mesh with others to transmit power.
Gear systems can transmit power between non-parallel, intersecting, and co-planar shafts.
|
Pros |
Cons |
|
|
To know the power transmission system to select for your system, it is crucial to factor the task to be accomplished, maintenance needs, and cost. You should also work with an expert.
